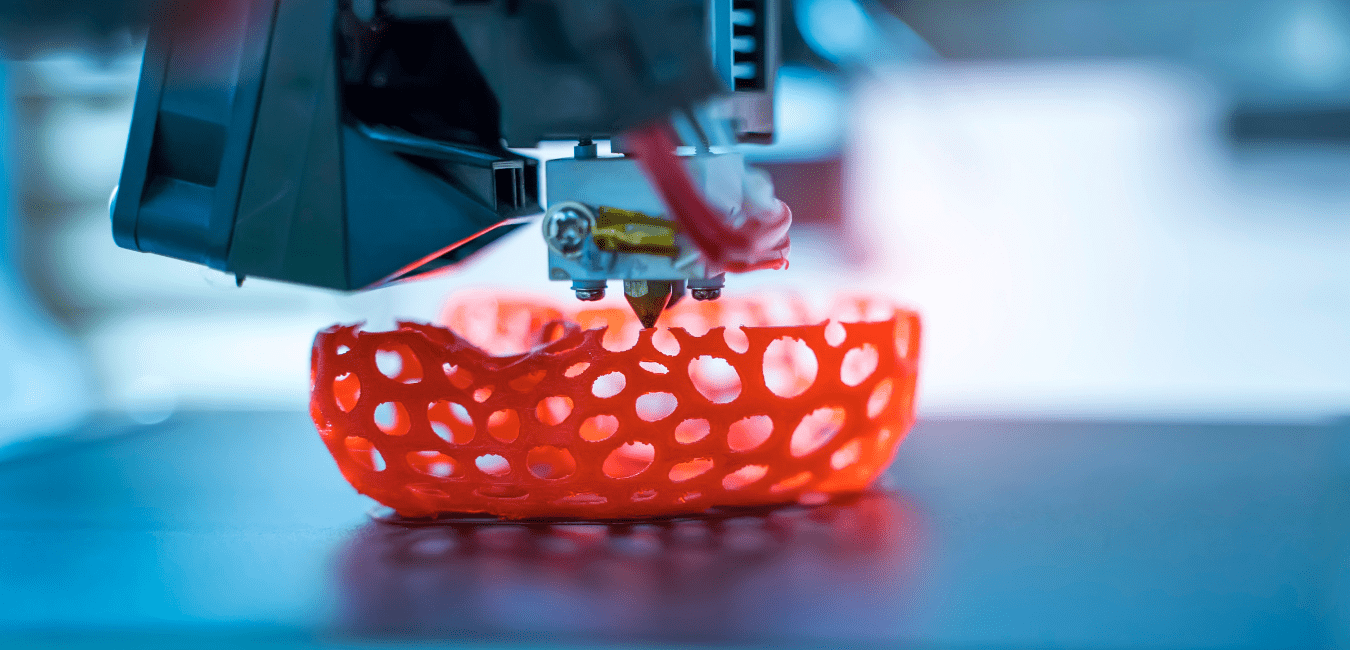
3D printing has emerged as one of the most revolutionary technologies of recent decades, transforming the way products are designed, developed and manufactured in various industrial sectors. This blog will explore what 3D printing is, its industrial applications and the exciting future prospects of this technology.
What is 3D Printing?
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a technology that allows you to create three-dimensional objects from digital models. Unlike traditional manufacturing methods that remove material, 3D printing builds objects layer by layer, adding material only where necessary.
How 3D Printing Works
The 3D printing process begins with the creation of a digital design using CAD (computer-aided design) modeling software. This design is converted into a file that the 3D printer can read. The printer then deposits material, which can be plastic, metal, resin or even biocompatible, layer by layer until the object is completed.
Types of 3D Printing Technology
There are several types of 3D printing technology, including:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Uses plastic filaments that are fused and extruded layer by layer.
- Stereolithography (SLA): Uses laser-cured liquid resin to form each layer.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Uses a laser to sinter material powder, fusing it layer by layer.
- Digital Light Processing (DLP): Similar to SLA, but uses a digital screen to cure the resin.
Industrial Applications of 3D Printing
Rapid Prototyping
One of the most common applications of 3D printing in industry is rapid prototyping. This process allows engineers and designers to produce physical models of their designs in a matter of hours, making it easy to verify form, fit and function before moving into mass production.
Custom Manufacturing
The ability of 3D printing to efficiently produce personalized objects has revolutionized industries such as medicine, where implants and prostheses can be made to measure for each patient. This customization also extends to fashion and jewelry, allowing for unique and personalized designs.
Small Series Production
For low-demand or limited edition products, 3D printing offers an economical solution. Companies can produce small series without the need to invest in expensive molds and tooling, thus reducing startup costs and time to market.
Functional Parts and Components
3D printing is used to manufacture functional parts and components that are difficult or impossible to produce with traditional methods. This includes complex parts for the aerospace, automotive and machinery industries, where precision and strength are crucial.
Maintenance and Repair
3D printing facilitates the production of spare parts on demand, which is especially useful in industries such as aerospace and maritime, where having specific parts available can be critical to operations. This reduces downtime and costs associated with maintenance and repair.
The Future of 3D Printing
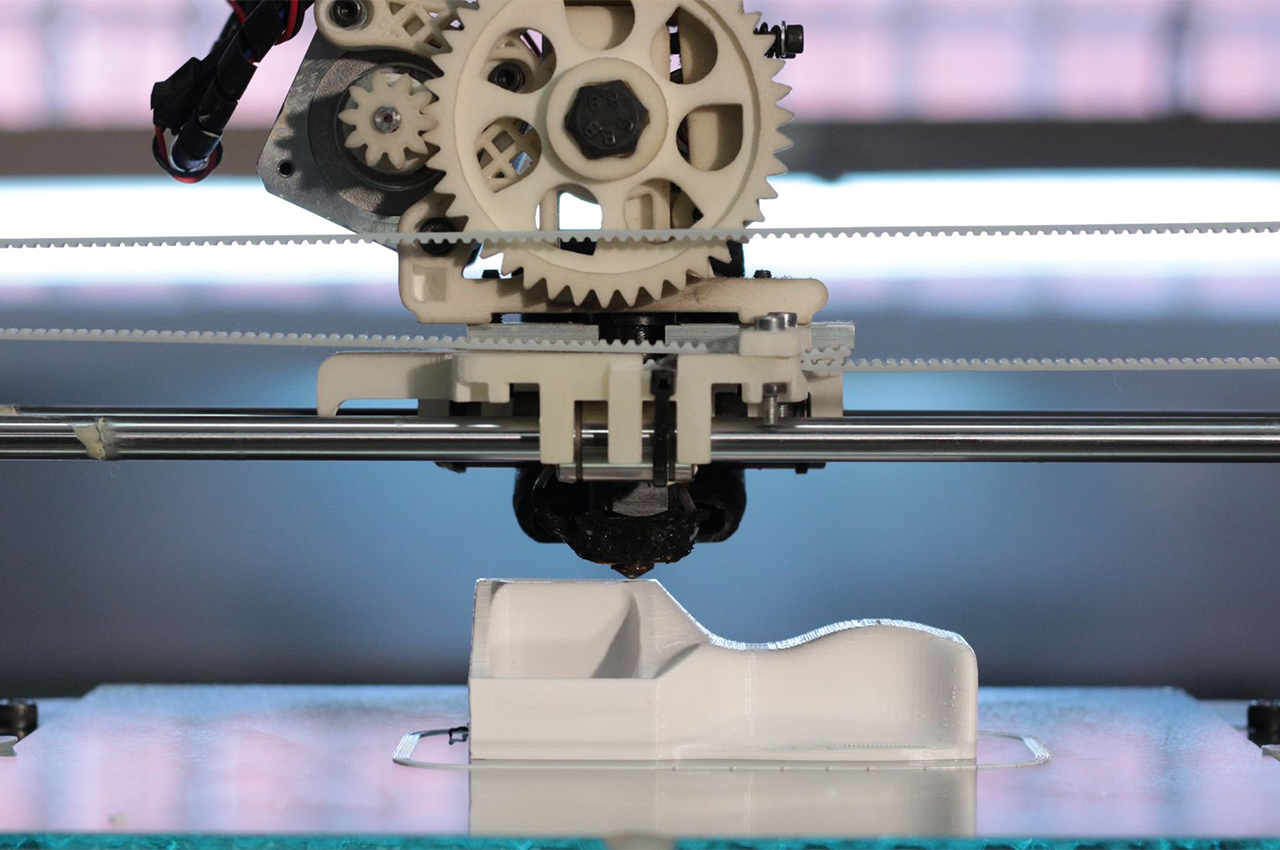

Innovations in Materials
The development of new materials is expanding the possibilities of 3D printing. In addition to traditional plastics and metals, advanced materials such as composites, ceramics and biocompatibles are being developed, which will allow even more varied and sophisticated applications.
Increased Speed and Efficiency
Technological innovations are improving the speed and efficiency of 3D printers. New printing techniques and hardware improvements enable faster production times, making additive manufacturing more viable for mass production applications.
Integration with Industry 4.0
3D printing is increasingly integrated with the concepts of Industry 4.0, which includes automation, the Internet of Things (IoT) and artificial intelligence. This integration will allow for smarter manufacturing, where 3D printers can be controlled and monitored remotely, optimizing the production process and reducing errors.
Advanced Medical Applications
In the medical sector, 3D printing has the potential to revolutionize the manufacturing of human organs and tissues. Although still in the research phase, 3D bioprinting promises to create functional organs for transplants, which could save countless lives and transform regenerative medicine.
Sustainability
3D printing also has the potential to be more sustainable than traditional manufacturing methods. By using only the material needed and allowing local production, waste and carbon emissions associated with transportation and logistics are reduced.
Conclusion
3D printing is revolutionizing industry and manufacturing, offering innovative solutions for prototyping, custom production, complex part manufacturing, and repair and maintenance. With the continued advancement of technology and the development of new materials, the future of 3D printing is incredibly promising.
If you want to explore the possibilities that 3D printing can offer your business, visit the Ibertronica 3D Printers to find the right tools that will help you innovate and improve your manufacturing processes.
As 3D printing continues to evolve, it will continue to transform various industries and open new opportunities for innovation and efficiency. The adoption of this technology can provide a significant competitive advantage, positioning companies at the forefront of advanced manufacturing.







